Sugar Diabetes
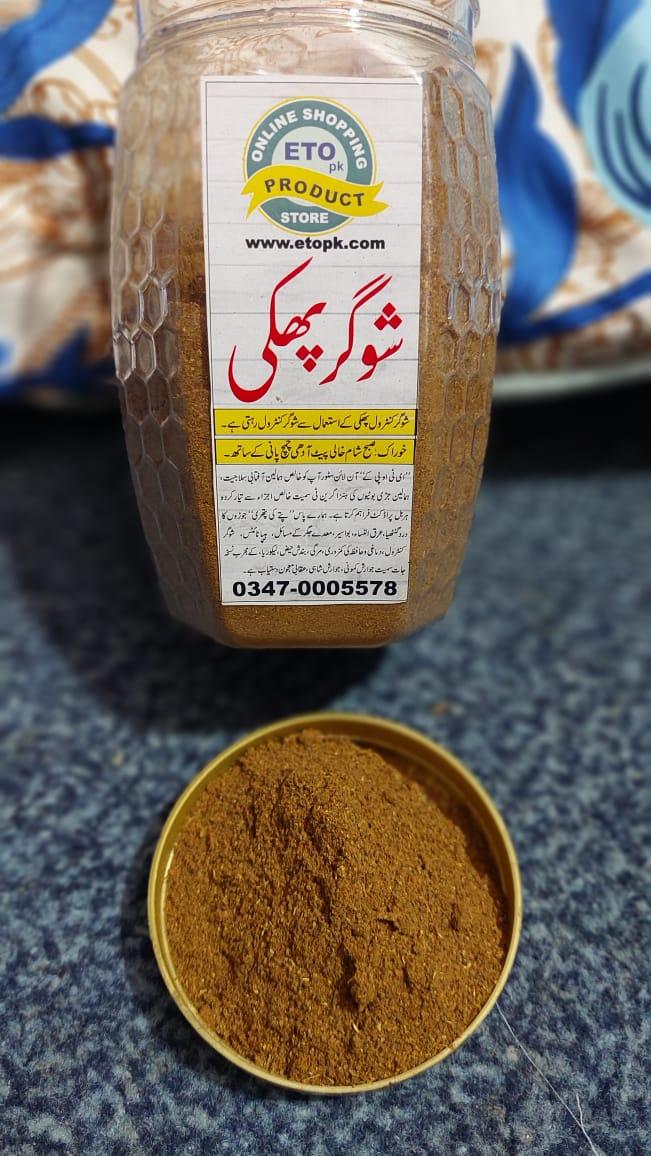
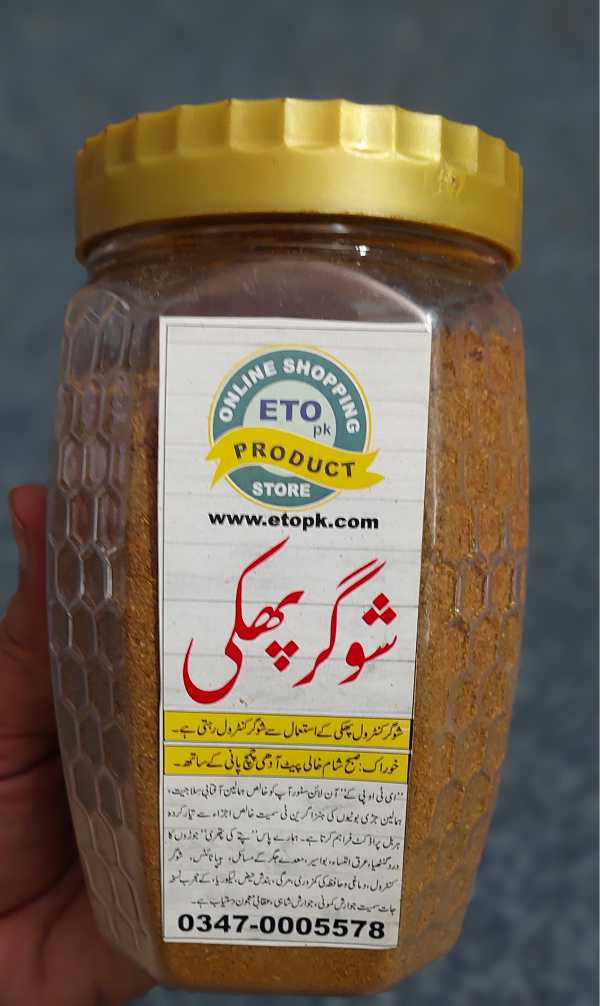
شوگر کنٹرول گولیاں
جس کے مسلسل استعمال سے شوگر کنٹرول رہتی ہے اور انگریزی میڈیسن کی ضرورت نہیں رہتی۔ اس کا چند ماہ تک مسلسل استعمال شوگر کو مکمل ختم بھی کرسکتا ہے۔
یہ بھی پڑھیں: Arthritis Joint Pain گنٹھیا جوڑوں کا درد
گردوں کی بچت
انگریزی گولیاں گردے خراب کرتی ہیں ان سے جان چھڑائیں، نیچرل ہربل شوگر کنٹرول گولیاں کھائیں، اگر شوگر بہت زیادہ پرانی نہیں تو چند مہینے استعمال سے ختم بھی ہو جاتی ہے۔
گھر بیٹھے حاصل کرنے کے لیے ابھی وٹس اپ کریں:

what is diabetes
Diabetes is a chronic medical condition that affects how the body processes blood sugar (glucose). Glucose is the main source of energy for the body’s cells, and insulin is a hormone that helps regulate glucose levels in the blood. In people with diabetes, the body either does not produce enough insulin or cannot use insulin effectively, leading to high blood sugar levels.
Over time, high blood sugar levels can damage organs and tissues in the body, leading to complications such as cardiovascular disease, nerve damage, kidney damage, eye damage, and poor wound healing. There are different types of diabetes, including type 1 diabetes, type 2 diabetes, and gestational diabetes, and each type may require different treatments. Diabetes is a lifelong condition, but with proper management and treatment, people with diabetes can lead healthy, active lives.
Types of Diabetes
There are three main types of diabetes:
- Type 1 diabetes: This type of diabetes is an autoimmune disease in which the body’s immune system attacks and destroys the insulin-producing cells in the pancreas. As a result, the pancreas produces little or no insulin, which is necessary to regulate blood sugar levels. Type 1 diabetes is usually diagnosed in children and young adults, although it can occur at any age.
- Type 2 diabetes: This type of diabetes occurs when the body becomes resistant to insulin or doesn’t produce enough insulin to regulate blood sugar levels. Type 2 diabetes is the most common type of diabetes and is often associated with lifestyle factors such as being overweight, inactive, or having a poor diet. It is usually diagnosed in adults, although it is increasingly being diagnosed in children and adolescents.
- Gestational diabetes: This type of diabetes occurs during pregnancy and usually goes away after delivery. Gestational diabetes can increase the risk of complications during pregnancy and delivery and can also increase the risk of developing type 2 diabetes later in life.
Precautions and Avoidance of Diabetes
There are several precautions and lifestyle changes that can help prevent or delay the onset of diabetes:
- Maintain a healthy weight: Being overweight or obese increases the risk of developing type 2 diabetes. Losing weight and maintaining a healthy weight through a balanced diet and regular physical activity can help reduce this risk.
- Follow a healthy diet: Eating a diet that is rich in whole grains, fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and healthy fats can help reduce the risk of diabetes. Avoiding sugary drinks, processed foods, and foods high in saturated and trans fats can also be helpful.
- Exercise regularly: Regular physical activity can help improve insulin sensitivity and lower blood sugar levels. Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise most days of the week.
- Quit smoking: Smoking increases the risk of diabetes, as well as other health problems. Quitting smoking can help reduce this risk.
- Limit alcohol consumption: Drinking alcohol can increase blood sugar levels and contribute to weight gain. Limiting alcohol consumption to moderate levels (no more than one drink per day for women and two drinks per day for men) can be helpful.
- Manage stress: Chronic stress can contribute to the development of diabetes. Finding healthy ways to manage stress, such as meditation, yoga, or exercise, can be beneficial.
- Get regular check-ups: Regular check-ups with a healthcare provider can help identify and manage risk factors for diabetes, as well as monitor blood sugar levels and other important health indicators.








Reviews
There are no reviews yet.